Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
Clark University
January, 1996
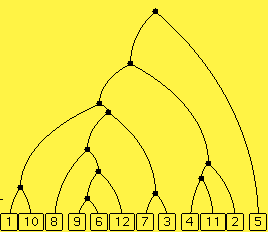
A node (dot) in the actual tree corresponds to a node in the reconstructed tree if they have exactly the same set of extant species as descendants. Those are the nodes that are drawn in black. All others are drawn in red.
Next page: the applet.
Previous page: reconstruction methods.
Table of contents: http://aleph0.clarku.edu/~djoyce/java/Phyltree.
David E. Joyce
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
Clark University
January, 1996